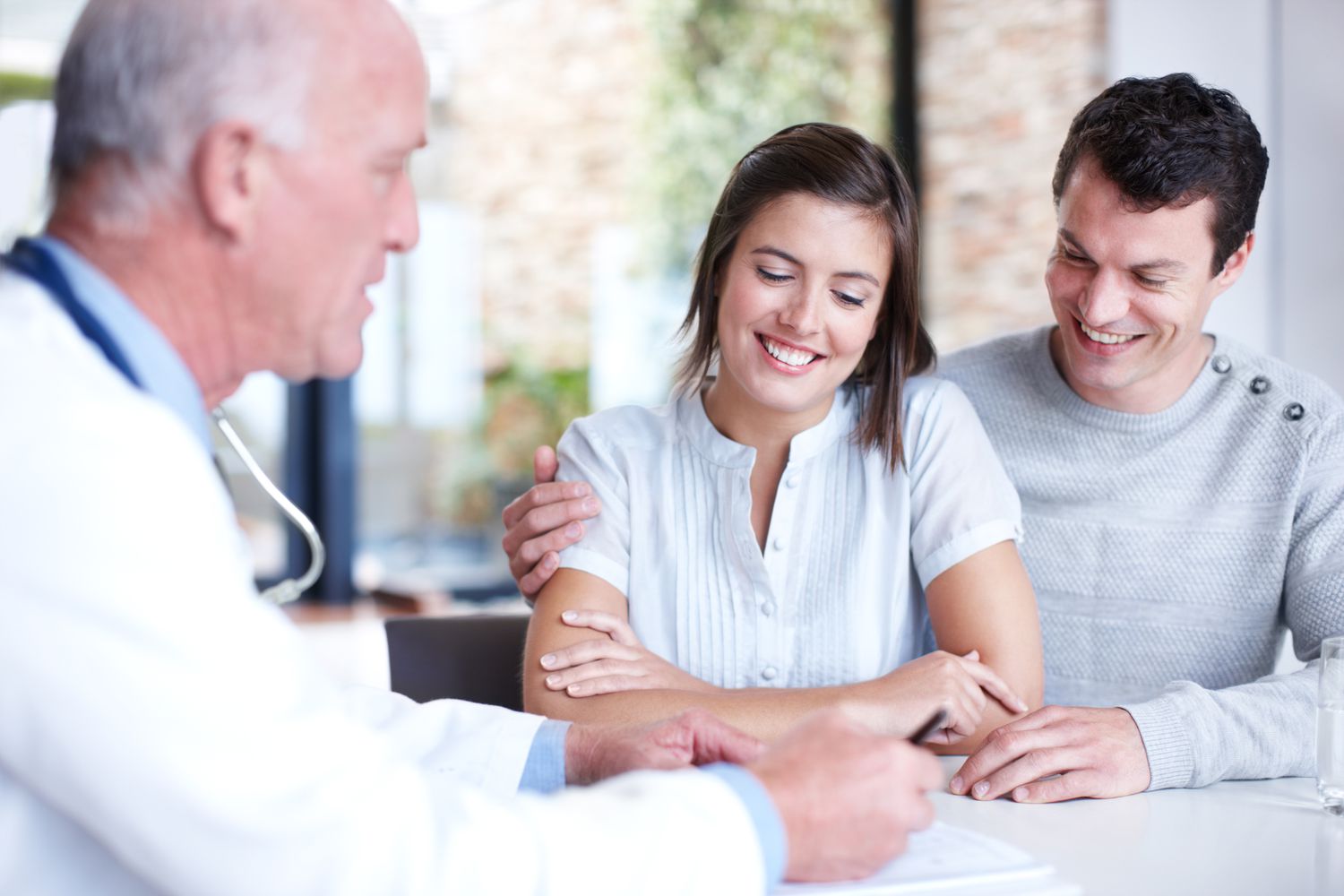
How to Access and Interpret Fertility Clinic Success Rates?
Whether you’re a Fertility Clinic In Patna or a patient looking for treatment, it’s important to know how to access and interpret success rates. Getting information about the success rate of your fertility clinic can make a big difference in your decision. You may be able to get information from your fertility clinic’s website or you may be able to access data from the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART).
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) include in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and embryo transfer. These procedures are used to treat a number of infertility issues.
For some couples, IVF is used in combination with other procedures, such as ICSI or gestational carrier. However, the success rate for these procedures may differ from one clinic to another.
Success rates vary based on several factors, including the patient’s age and the reason for infertility. However, studies have shown that the overall success rate for IVF increases with age.
Using IVF, a woman can conceive a healthy baby. It is used to treat a number of infertility conditions, including endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, and diminished ovarian reserve.
In a full cycle of IVF, a woman’s ovaries are stimulated to produce multiple eggs. A single healthy sperm is then injected into each egg. This results in a viable embryo that is transferred into the uterus.
IVF can result in multiple pregnancy
During IVF treatment, more than one embryo is transferred to the uterus. The number of embryos transferred is typically based on the age of the patient.
Multiple births have the potential to increase the risk of premature delivery, low birth weight, still birth, neonatal death and gestational diabetes. This puts an enormous burden on families and the NHS. Various approaches have been used to reduce the multiple birth rate. The HFEA has developed a strategy for IVF clinics to minimise the multiple birth rate.
The HFEA developed a series of workshops to help fertility clinics share their experiences and learn from each other. It also facilitated the dissemination of best practice. In 2006, an Expert Group on Multiple Births after IVF was established. Its report, ‘One Child at a Time’, was published.
IVF is the most common treatment for severely damaged or absent fallopian tubes
Assisted reproductive technology includes gamete intrafallopian transfer and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Both techniques have been used to treat infertility in women with tubal problems.
In IVF, a healthcare provider stimulates a woman’s ovaries to produce multiple eggs. These eggs are then fertilized by sperm. The success of the treatment depends on the number of eggs transferred, the age of the woman, and the type of treatment.
The success rate of IVF is generally around 18 percent per cycle. However, it can be higher depending on the health history of the patient. It is also expensive and may increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and multiple births.
Before starting the treatment, a woman should be screened for HIV, ovarian cysts, and endometriosis. She may also be prescribed hormone injections to stimulate her ovaries.
SART reports IVF outcome data for 90% of the fertility clinics in the country
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) is a group of treatments used to help infertile couples conceive children. These treatments include in vitro fertilization, tubal embryo transfer, and gamete intrafallopian transfer. Some ART treatments are more invasive than others.
ART success rates vary from clinic to clinic, and may be influenced by the characteristics of the patient. Some factors that may affect IVF outcome include female age, ovarian reserve, ovulatory dysfunction, and comorbidities. Several preprocedure factors may also influence the outcome of an IVF cycle.
In the United States, there are different IVF success rates depending on the race and ethnicity of the patient. These differences likely reflect true biological and socioeconomic differences. The highest live birth rates are found among females with ovulatory dysfunction.
SART regulates how individual clinics publish their pregnancy outcome data
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) programs are required by law to report their successes and failures. The data is collected by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) through the National ART Surveillance System (NASS). The NASS is a web-based system that provides a central repository for information about ART.
Also Read: Why Fertility Counselling is More Important?
The NASS provides valuable information about ART practices, but it’s not the only resource of its kind. In 2010, HHS/CDC collected data from approximately three-quarters of all ART programs in the country. To make sense of the data, HHS/CDC opted for an empirical study. In the study, they examined 812,400 cycles, encompassing an estimated two million patients. HHS/CDC selected a random sample of five to 10 percent of all reporting ART programs to test the system’s ability to collect and organize data.
Read More: Modern dental surgery and solutions